CO2-philic polymer membrane with high separation performance
W. Yave, A. Car, S. S. Funari, S.P. Nunes, K.V. Peinemann
Macromolecules 43 (1), 326-333, (2010)
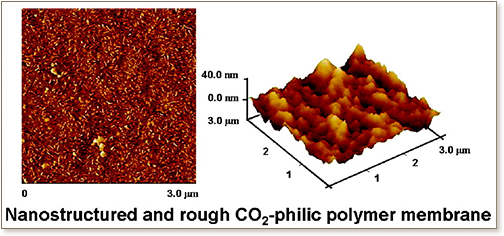
Polymeric membranes are attractive for CO2 separation and concentration from different gas streams because of their versatility and energy efficiency; they can compete with, and they may even replace, traditional absorption processes. Here we describe a simple and powerful method for developing nanostructured and CO2-philic polymer membranes for CO2 separation. A poly(ethylene oxide)−poly(butylene terephthalate) multiblock copolymer is used as membrane material. Smart additives such as polyethylene glycol dibutyl ether are incorporated as spacers or fillers for producing nanostructured materials. The addition of these specific additives produces CO2-philic membranes and increases the CO2 permeability (750 barrer) up to five-fold without the loss of selectivity. The membranes present outstanding performance for CO2 separation, and the measured CO2 flux is extremely high (>2 m3 m−2 h−1 bar−1) with selectivity over H2 and N2 of 10 and 40, respectively, making them attractive for CO2 capture.