PVDF hollow fiber and nanofiber membranes for fresh water reclamation using membrane distillation
L. Francis, N. Ghaffour, A.S. Alsaadi, S.P. Nunes, G.L. Amy
Journal of Materials Science, 49 (5), pp. 2045-2053, (2014)
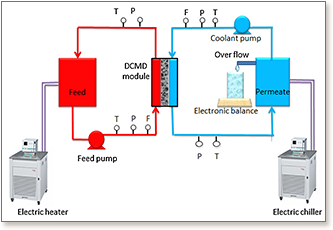
Polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber and nanofibrous membranes are engineered and successfully fabricated using dry-jet wet spinning and electrospinning techniques, respectively. Fabricated membranes are characterized for their morphology, average pore size, pore size distribution, nanofiber diameter distribution, thickness, and water contact angle. Direct contact membrane distillation (DCMD) performances of the fabricated membranes have been investigated using a locally designed and fabricated, fully automated MD bench scale unit and DCMD module. Electrospun nanofibrous membranes showed a water flux as high as 36 L m−2 h−1 whereas hollow fiber membranes showed a water flux of 31.6 L m−2 h−1, at a feed inlet temperature of 80 °C and at a permeate inlet temperature of 20 °C.